
It is a chronic disease that occurs either when the pancreas does not produce enough insulin or when the body cannot effectively use the insulin it produces. Over time, having too much glucose in our blood can cause health problems. Although it has no cure, we can take steps to manage it and stay healthy. Hyperglycaemia (or raised blood sugar) is a common effect of uncontrolled diabetes and over time leads to serious damage to many of the body's systems, especially the nerves and blood vessels.
In 2014, 8.5% of adults aged 18 years and older had diabetes. In 2016, it was the direct cause of 1.6 million deaths and in 2012 high blood glucose was the cause of another 2.2 million deaths.
TYPES of Diabetes
- Type 1 Diabetes : Also known as juvenile diabetes, is an autoimmune disease. Type 1 diabetes results from the pancreas's failure to produce enough insulin due to loss of beta cells. Our immune system attacks and destroys the cells in our pancreas that make insulin. Type 1 diabetes is usually diagnosed in children and young adults, although it can appear at any age. People with type 1 diabetes need to take insulin every day to stay alive. About 10% of people with diabetes have this type. The cause of this autoimmune response is unknown.
- Type 2 Diabetes : Type 2 diabetes begins with insulin resistance, a condition in which cells fail to respond to insulin properly. We can develop type 2 diabetes at any age, even during childhood. However, this type of diabetes occurs most often in middle-aged and older people. This is the most common type of diabetes, according to the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, and it has strong links with obesity.
- Gestational Diabetes : Gestational diabetes develops in some women when they are pregnant. Insulin-blocking hormones produced by the placenta cause this type of diabetes. Most of the time, this type of diabetes goes away after the baby is born. However, if we’ve had gestational diabetes, we have a greater chance of developing type 2 diabetes later in life. Sometimes diabetes diagnosed during pregnancy is actually type 2 diabetes.
SIGNS & SYMPTOMS of Diabetes
- General Symptoms :--
· increased hunger (polyphagia)
· increased thirst (polydipsia)
· weight loss
· frequent urination (polyuria)
· blurry vision
· extreme fatigue
· sores that don’t heal
· numbness or tingling in the feet or hands
Symptoms may develop rapidly (weeks or months) in type 1 diabetes, while they usually develop much more slowly and may be subtle or absent in type 2 diabetes.
- Symptoms in Men :--
- Symptoms in Women :--
- Symptoms of type 1 diabetes include:
It may also result in mood changes.
- Symptoms of type 2 diabetes include:
It may also cause recurring infections. This is because elevated glucose levels make it harder for the body to heal.
Symptoms of type 1 diabetes can start quickly, in a matter of weeks. Symptoms of type 2 diabetes often develop slowly—over the course of several years—and can be so mild that we might not even notice them. Many people with type 2 diabetes have no symptoms. Some people do not find out they have the disease until they have diabetes-related health problems, such as blurred vision or heart trouble.
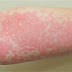
Several other signs and symptoms can mark the onset of diabetes although they are not specific to the disease. Prolonged high blood glucose can cause glucose absorption in the lens of the eye, which leads to changes in its shape, resulting in vision changes. Long-term vision loss can also be caused by diabetic retinopathy. A number of skin rashes that can occur in diabetes are collectively known as diabetic dermadromes.
People (usually with type 1 diabetes) may also experience episodes of diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA), a metabolic disturbance characterized by nausea, vomiting and abdominal pain, the smell of acetone on the breath, deep breathing known as Kussmaul breathing, and in severe cases a decreased level of consciousness.
No comments:
Post a Comment
Please do not enter any spam link in the comment box.